Human Motor Neuron Data
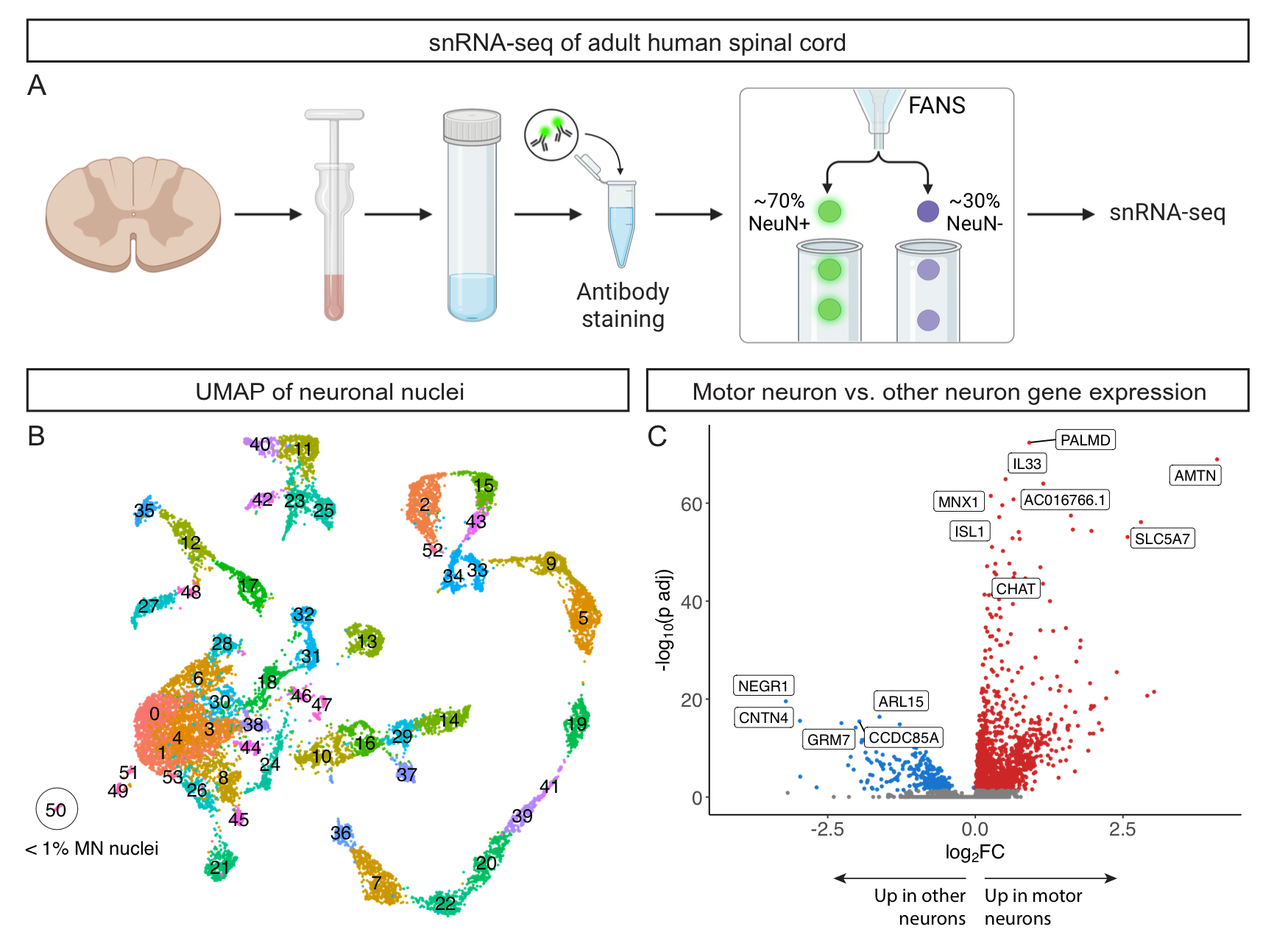
A recent paper detailing the transcriptomic diversity of the spinal cord made suggested that motor neurons were more abundant than expected, diverged highly from mouse motor neurons, and were heavily enriched for cytoskeletal transcripts implicated in ALS. Here we report contradictory results--that human motor neurons are rare in the spinal cord, can be divided into known subtypes, and share a common signature with mouse motor neurons. We further re-analyzed their data and provide evidence that their conclusions about motor neurons are the result of a technical artifact in the data. Please see read more on biorxiv here. We have made all of our sequencing data available on GEO, and all R objects are available for download from this site in the "More Information" tab. All analysis code is available on our GitHub repository
Read MorePichon Lab Paper is out in Nature Comm!

We are pleased to announce that the Le Pichon lab has recently published their single-nucleus cholinergic sequencing data in Nature Communications! Their data is featured on this site, and available to download as an integrated resource along with our (Gitler Lab) data. Big congratulations to Alkaslasi et al. for a fantastic and impactful paper! Read it here!
Read MoreData Integration with the Le Pichon Lab!
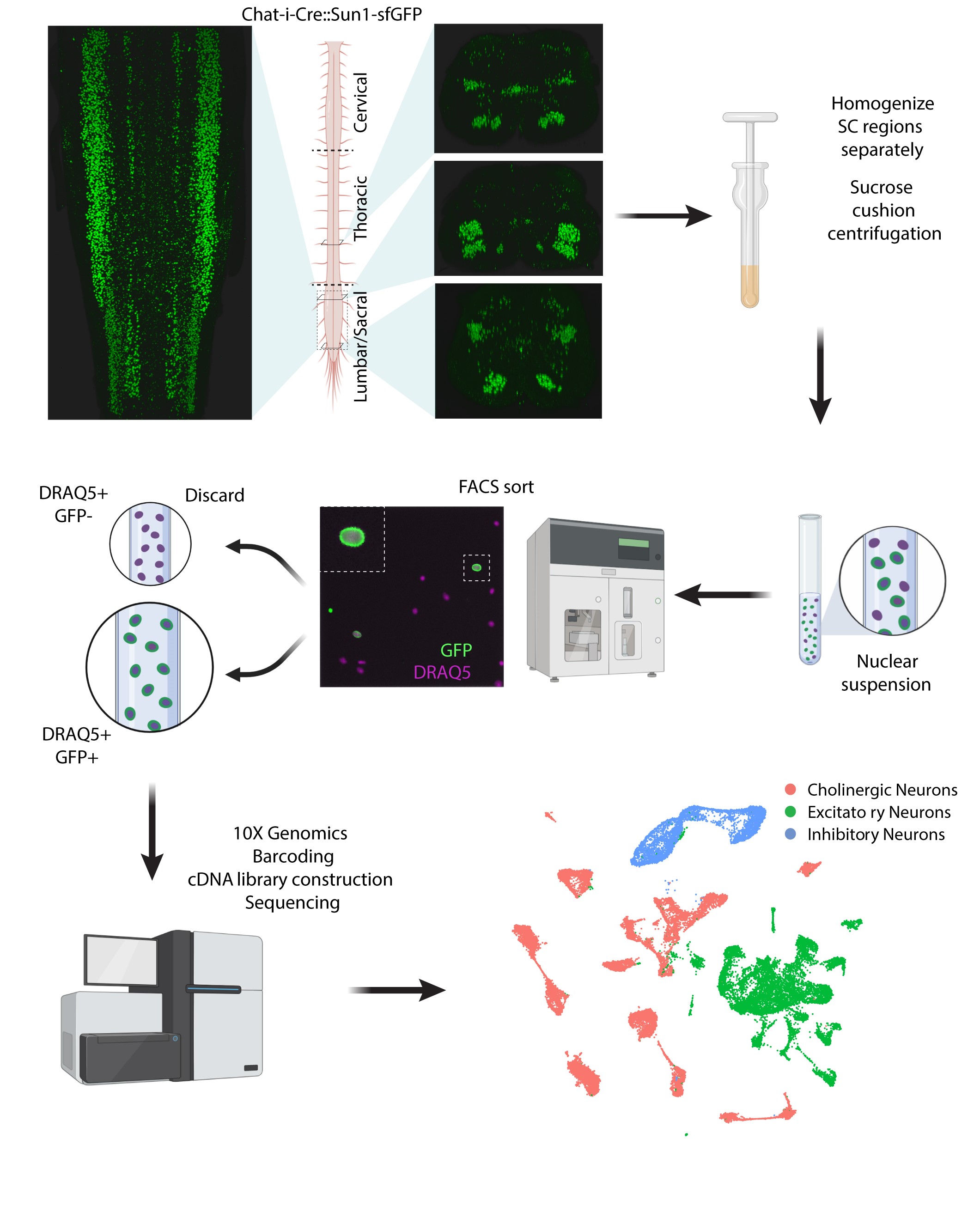
We are very excited to announce that we have gotten together with Claire Le Pichon's Lab , who used different methods to perform similar experiments in parallel to our work. While the markers that they chose to validate were slightly different from ours, the data are extremely concordant and reinforce the fundamental nature of our collective findings. We are currently working to integrate the datasets and make them all publicly available for browsing via cellxgene, as well as for download as a processed and integrated file. Look out for more exciting work from the Le Pichon lab moving forward, and follow Dr. Le Pichon and first authors Mor Alkaslasi and Zoe Piccus on twitter!
Read MoreProcessed matrix download links
We have received several comments from collaborators and interested parties that the raw .h5 and .fastq formats that we made available on GEO are unnecessarily cumbersome, as they require a large amount of computing power to integrate and cluster a large number of cells. To streamline data sharing, we have added a Download link for the processed .h5d matrices (with cluster ID and annotations) in a .zip file. This link has also been added to the Downloads bar on the More Information tab!
Read More